Sealless centrifugal pump is divided into shielded motor drive and magnetic drive two structures, and has many years of experience. However, the sealless rotor pump only started to be used in recent years. This article will be positive displacement pump and magnetic drive technology combined with the structure and advantages are discussed. In the process industry, magnetically driven pumps are gaining more and more widespread use. When choosing a magnetically driven pump, not only safety considerations, but also its ability to prevent leaks and the need to reduce maintenance are increasingly becoming important factors. When calculating Total Life Cycle Cost, a magnetically driven pump can often provide the most economical solution. Whenever magnetic drive pumps are discussed, the following points are often referred to as disadvantages compared to mechanical seal pumps: complex construction; failure to exceed their maximum torque, even in short periods of time; more expensive; especially when introduced for the first time Magnetically driven pumps, often mentioned above point of view. A related issue is what progress has been made in magnetic drive technology in the promotion phase? From the fact that more and more people use magnetic-driven pumps, we can infer that magnetic drive technology has made great strides. The design of the current design are based on the application of experience developed from. This gives the pump a rather simple and robust construction that gives the magnetically driven pump exactly the same reliability as a mechanically sealed pump. As much as possible to extend the interval between the two major repairs is very important, so reliability has become a basic focus of design and development now. Reducing wear between the two magnetic couplings while enhancing cooling means that magnetically driven pumps offer the most optimized solution in more applications than ever before. A typical example is that a manufacturer has adopted a proven patented technology to overcome the resistance loss, overheating and wear of the inner bearing chamber. This is achieved by balancing the fluid in the pump with the following working principle: There are radial holes in the rotor connected to the hollow shaft. During operation, centrifugal force acts on the liquid in the radial bore, creating a negative pressure in the hollow shaft associated with the magnetically driven portion. The pressure differential promotes fluid circulation in two separate cavities behind the rotor, effectively removing the heat generated by friction and magnetic losses. These cavities are connected to the inlet and outlet, respectively. Compared with other magnetically driven pumps, this system retains the pump's original good self-priming capability because "cooling fluid" does not short the inlet and outlet directly. Sufficient cooling liquid is generated independently of the pressure at the inlet and outlet, viscosity and shaft speed. Moreover, one of the more important and unique advantages of this system is that the manufacturer's ROTAN magnetically driven gear pump can be reversed without affecting the operation of its cooling system. Because of the reversal, the flow of liquid in the system is just the opposite of the simple one. In an internal gear pump, it is important to maintain control of the axial clearance (ie, the distance between the rotor end face and the pump head end cap). In ROTAN-designed magnetically driven pumps, axial clearance control is achieved with two face-to-face thrust bearings. This design minimizes bearing loads, reducing wear and extending service life. This is also achieved by the above-mentioned chambers that produce hydraulic thrust equal to the forward end of the rotor to maintain the balance. In summary, these design features ensure reduced maintenance times and eliminate the possibility of seal failures that normally result in pump downtime. Torque Limit When selecting a positive displacement pump, it is important to get the correct fluid viscosity data. An increase in viscosity will result in higher pressure and liquid "drag" on the pump. A common pump overcomes the added resistance of a temporary increase in viscosity, but a magnetically driven pump will fail magnetic coupling when the torque exceeds the maximum torque of the magnetic drive. Coupling failure is undesirable because it creates additional heat inside the pump and accumulates, quickly causing damage to the magnet. Pump set safety valve can play a protective role to prevent coupling failure, but the best way is to ensure that the magnet has enough torque margin. Some progress has also been made technically in this regard: the cost of magnet materials has been declining year-on-year in the past few years. At the same time, the magnetism of the existing magnet is increasing, which means that the magnet torque increases significantly without increasing the cost and size. In other words, the current pump has a greater safety factor than before, even at maximum pressure. For large pumps, generally use a higher level of magnet than the usual requirements. This will inevitably increase some costs, but there will be a marked improvement in safety. Expenses In general, a magnetically driven pump can cost more to buy than a normal pump with a single mechanical seal. Magnetically driven pumps, however, often prove to be the more economical solution when taking into account the reduced maintenance costs, while taking into account the savings in other costs associated with magnetically driven pumps. In general, a stainless steel magnetically driven pump is about 30% more expensive than a pump of the same size and with a single seal. But in the first year or two shut down maintenance and mechanical seal replacement will cost this difference. Magnetically-driven pumps tend to be less expensive to buy than more expensive forms of seals, such as dual-mechanical seals, double or single-cartridge mechanical seals, or gas-tight seals. Conclusion In recent years, magnetically driven pumps have developed rapidly. A great deal of research and development resources have been and will continue to be applied to this technology. The cost of magnet materials will continue to decrease while its strength will continue to increase. Existing magnetically driven pumps have the same reliability as normal pumps, with the weakest parts removed, such as not being sealed here. In addition, the overall price of magnetic drive pumps is on a downward trend. Obviously, the magnetic coupling technology applied to the rotor pump will gradually increase, and will gradually replace the mechanical seal with the pump.
This series of permanent-magnet synchronous gearless traction machines is directly driven by a low-speed, high-torque, 3-phase permanent magnet synchronous motor, and has the advantages of low energy consumption, low noises, no pollution, and little maintenance.
By using flat frame structure with three mounting surfaces, this series of traction machines can be installed on bottom floor or any middle positions or on the top of shaft way.
These traction machines can be arranged for providing upward traction or downward traction, and have remote manual brake release function. Wrap angle of the traction machines can be only 180°.
Standard Gearless Traction Elevator, Gearless Elevator Traction Machine, Gearless Elevator Machine, Gearless Traction Motor
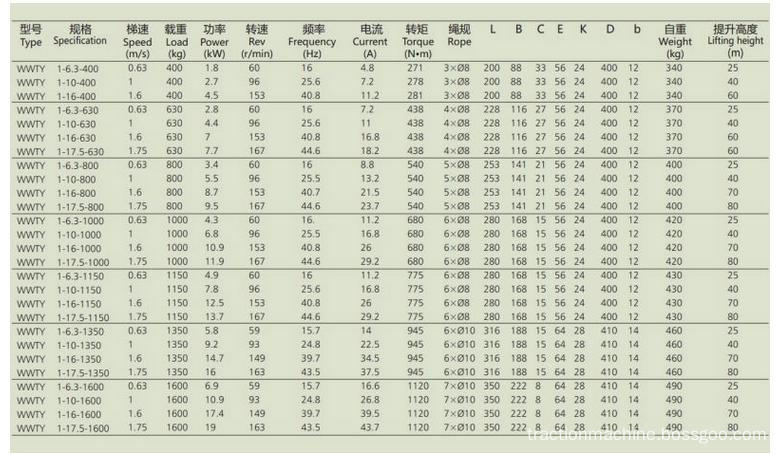
Gearless Traction Machine
Gearless Traction Machine,Gearless Traction Elevator, Gearless Elevator Traction Machine, Gearless Elevator Machine, Gearless Traction Motor
Ningbo Xinda Elevator Traction Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.nbelevator.de
